UNITI

Unification of treatments and Interventions for Tinnitus patients
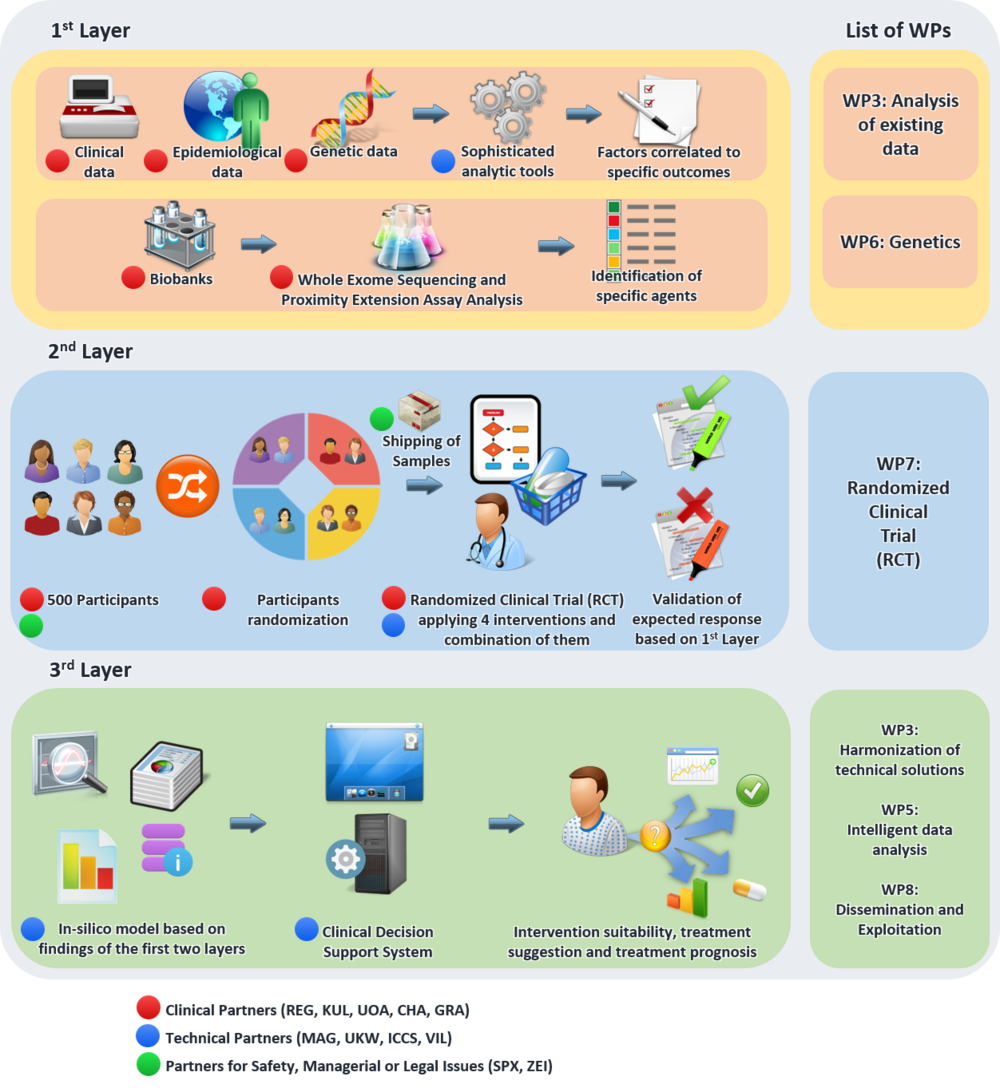
Tinnitus is the perception of a phantom sound and the patient’s reaction to it. Tinnitus remains a scientific and clinical enigma of iTinnitus is the perception of a phantom sound and the patient’s reaction to it. Although much progress has been made, tinnitus remains a scientific and clinical enigma of high prevalence and high economic burden. It affects more than 10% of the general population, whereas 1% of the population considers tinnitus their major health issue. Recent cohort studies show that tinnitus prevalence tends to increase over time and with older age. Assuming that there is no cure to be found, the prevalence estimates in Europe would double by 2050. A large variety of patient characteristics - including genotyping, aetiology, and phenotyping - are poorly understood, because integrated systems approaches are still missing to correlate patient`s characteristics to predict responses to combinatorial therapies.
Although genetic causes of tinnitus have been neglected for decades, recent findings of genetic analysis in specific subgroups (gender and phenotype) have highlighted that bilateral tinnitus in men reached a heritability of 0.68. This heritability is close to autism, schizophrenia and Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD). There is no current consensus on tinnitus treatment. UNITI’s overall aim is to deliver a predictive computational model based on existing and longitudinal data attempting to address the question which treatment approach is optimal for a specific patient based on specific parameters. Clinical, epidemiological, medical, genetic and audiological data, including signals reflecting ear-brain communication, will be analysed from existing databases. Predictive factors for different patient groups will be extracted and their prognostic relevance will be tested in a randomized controlled trial (RCT) in which different groups of patients will undergo a combination of therapies targeting the auditory and central nervous systems.
Teilnehmende Institute und Kliniken
| Nr | Name | Abkürzung | Land |
|---|---|---|---|
1. | KLINIKUM DER UNIVERSITAET REGENSBURG | UHREG | Deutschland |
2. | KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN | KUL | Belgien |
3. | ETHNIKO KAI KAPODISTRIAKO PANEPISTIMIO ATHINON | UOA | Griechenland |
4. | CHARITE - UNIVERSITAETSMEDIZIN BERLIN | CHA | Deutschland |
5. | SERVICIO ANDALUZ DE SALUD | GRA | Spanien |
6. | KAROLINSKA INSTITUTET | KI | Schweden |
7. | OTTO-VON-GUERICKE-UNIVERSITAET MAGDEBURG | MAG | Deutschland |
8. | UNIVERSITAETSKLINIKUM WUERZBURG - KLINIKUM DER BAYERISCHEN JULIUS-MAXIMILIANS- UNIVERSITAET | JMU | Deutschland |
9. | INSTITUTE OF COMMUNICATION AND COMPUTER SYSTEMS | ICCS | Griechenland |
10. | ISTITUTO DI RICERCHE FARMACOLOGICHE MARIO NEGRI | MIL | Italien |
11. | VILABS (CY) LTD | VIL | Zypern |
12. | SPHYNX TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS AG | SPX | Schweiz |
13. | ZEINCRO EGESZSEGUGYI SZOLGALTATO KORLATOLT FELELOSSEGU TARSASAG | ZEI | Ungarn |
Publikationen
-
. Single versus combination treatment in tinnitus: an international, multicentre, parallel-arm, superiority, randomised controlled trial. Nature Communications [Internet]. 2025;. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-66165-1
- [ DOI ]
-
. Pilot study of a smartphone-based tinnitus therapy using structured counseling and sound therapy: A multiple-baseline design with ecological momentary assessment. PLOS Digital Health [Internet]. 2023;2(1):e0000183. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pdig.0000183
- [ DOI ]
-
. A Similarity-Guided Framework for Error-Driven Discovery of Patient Neighbourhoods in EMA Data. In: Crémilleux B, Hess S, Nijssen S, editors. Advances in Intelligent Data Analysis XXI. Springer Nature Switzerland; 2023. pp. 459-71.
- [ DOI ]
-
. Predicting Patient-Based Time-Dependent Mobile Health Data. In: 2023 IEEE 36th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS). 2023. pp. 79-84.
- [ DOI ]
-
. Exploring Concepts for Pipeline-Driven Mobile Health Data Dashboards: Insights from Personal Projects and GitHub Contributions. In: 2023 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI). 2023. pp. 1344-50.
- [ DOI ]
-
. Towards a unification of treatments and interventions for tinnitus patients: The EU research and innovation action UNITI. In: Schlee W, Langguth B, Kleinjung T, Vanneste S, De Ridder D, editors. Progress in Brain Research [Internet]. Elsevier; 2021. pp. 441-5. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0079612320302351
- [ DOI ]
-
. Using Big Data to Develop a Clinical Decision Support System for Tinnitus Treatment. In: Searchfield GD, Zhang J, editors. The Behavioral Neuroscience of Tinnitus [Internet]. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2021. pp. 175-89. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/7854_2021_229
- [ DOI ]
-
. UNITI Mobile—EMI-Apps for a Large-Scale European Study on Tinnitus. In: 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). 2021. pp. 2358-62.
- [ DOI ]